Looking for extraordinary buildings that push design boundaries? Here's what you need to know about the world's most striking architectural designs:
Key buildings covered:
- Guggenheim Museum (Bilbao) - Titanium waves that revitalized a city
- Sydney Opera House - Shell-like sails that define Australia's identity
- Marina Bay Sands - Three towers topped by a 340m floating platform
- Lotus Temple - 27 marble petals forming a giant lotus flower
- Dancing House - Twin towers mimicking dancers in motion
Why these matter:
- They blend art and engineering in groundbreaking ways
- Many transformed their cities' economies and culture
- Each pioneered new construction techniques
- All have become iconic landmarks
Modern architectural innovations:
- AI and 3D software enabling complex designs
- New materials like ETFE panels weighing 1% of glass
- 3D printing entire buildings in days
- Green technology integration
Want to analyze buildings yourself? Try Architecture Helper - an AI tool that identifies styles and design elements from photos.
| Building Type | Key Innovation | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Deconstructivist | Fragmented shapes | Challenges traditional forms |
| Future-focused | Science-inspired | Pushes engineering limits |
| Sustainable | Green integration | Reduces environmental impact |
| Experimental | Unusual forms | Creates memorable landmarks |
Bottom line: Today's architecture goes beyond aesthetics to reshape cities, drive innovation, and address environmental challenges while creating unforgettable spaces.
Related video from YouTube
Famous Buildings That Stand Out
Some buildings go beyond functional use, blending art and engineering in ways that leave a lasting impression. These structures reshape cityscapes and inspire awe, often becoming iconic landmarks celebrated worldwide.
Guggenheim Museum, Bilbao, Spain
Frank Gehry's creation transformed Bilbao when it debuted in 1997. Known for its flowing, metallic design, the structure reflects the city's industrial roots while mirroring the natural curves of the Nervión River. Its titanium surface interacts with light throughout the day, resulting in a dynamic and ever-changing facade that helped uplift the city.
"The Guggenheim Museum represents a perfect harmony between the city's industrial past and its artistic future", says architect Frank Gehry. The museum's debut sparked the "Bilbao Effect", a term used to describe urban regeneration influenced by bold architecture.
Sydney Opera House, Australia
As an unmistakable symbol of Australia, this UNESCO World Heritage Site stands out for its breathtaking design and engineering challenges. Jørn Utzon completed the project in 1973, crafting its unique roof from 2,194 pre-cast concrete segments that resemble shells. Situated by Sydney Harbor, the Opera House seems to float, blending seamlessly into its surroundings.
Marina Bay Sands, Singapore
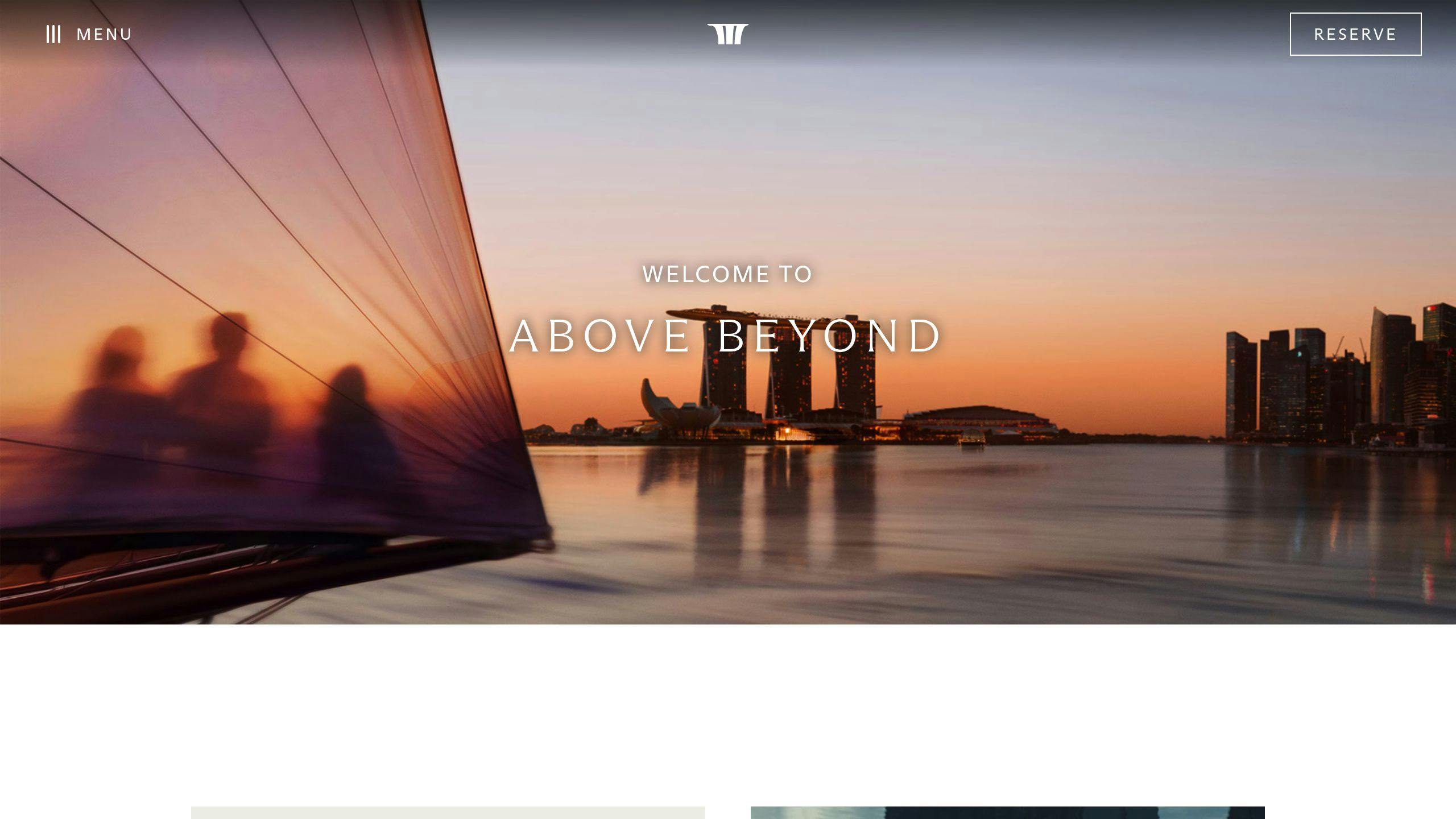
Designed by Moshe Safdie, this architectural marvel changed Singapore's skyline when it opened in 2011. Its three towering structures are connected by the SkyPark, a dramatic 340-meter-long platform featuring a 150-meter infinity pool. From this height, visitors enjoy unparalleled views of the city, making it both an engineering triumph and a luxury destination.
Lotus Temple, New Delhi, India

Fariborz Sahba’s design for the Lotus Temple captures the spirit of the Bahá'í faith. Completed in 1986, the temple's design features 27 marble "petals", grouped in clusters of three to form nine sides, creating a stunning lotus-like appearance. The building has become a symbol of serenity and unity, representing religious architecture at its finest.
Dancing House, Prague, Czech Republic
Built in 1996, this standout creation by Frank Gehry and Vlado Milunić challenges traditional design in a city known for its historic charm. Nicknamed "Fred and Ginger", the structure features two towers that mimic the motion of dancers, making it a stark yet captivating contrast to Prague's classic baroque skyline.
| Building | Year Completed | Key Feature | Architect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guggenheim Museum | 1997 | Shimmering titanium exterior | Frank Gehry |
| Sydney Opera House | 1973 | Iconic tiled shell-like roof | Jørn Utzon |
| Marina Bay Sands | 2011 | SkyPark with infinity pool | Moshe Safdie |
| Lotus Temple | 1986 | Flower-shaped marble design | Fariborz Sahba |
| Dancing House | 1996 | Dynamic twin-tower silhouette | Gehry & Milunić |
Building Styles That Break the Mold
Architecture keeps moving forward, leaving behind dated designs and pushing boundaries in how structures are imagined and built. Here’s a look at some styles that challenge what we think buildings should be.
Deconstructivism: Controlled Chaos
Deconstructivism burst onto the scene in the 1980s, offering a sharp contrast to clean, orderly design. This style embraces fragmented shapes and unconventional geometry, resulting in buildings that look like they’ve stepped out of a dream. Architects like Zaha Hadid and Frank Gehry are known for projects that appear almost gravity-defying, creating works that feel like art as much as architecture.
"Architecture is not just one thing. It is not just an art. … It has to deal with the real situation; it has to do something good for the society." - Xiaodu Liu, ArchDaily
The Future in Focus
Future-focused design brings tomorrow’s ideas to life right now. A standout example is Belgium’s Atomium, constructed for the 1958 World’s Fair. At 102 meters tall, this structure represents an iron crystal magnified 165 billion times, blending the worlds of science and architecture in a way that remains mesmerizing decades later.
Brutalism: Raw and Bold
Brutalism makes no apologies for its use of raw concrete, delivering unapologetically bold architectural statements. Habitat 67 in Montreal is a perfect example. This residential complex uses modular concrete units in a stacked design, creating a space that’s both functional and visually powerful. It’s a style that often divides opinion but undeniably commands attention.
The Present-Day Focus
Modern buildings are evolving to address global concerns like sustainability, blending innovation with responsible design. Milan’s Bosco Verticale, or Vertical Forest, exemplifies this shift. Its facade is adorned with over 900 trees and 2,000 plants, combining functional environmental benefits with striking visuals.
| Architectural Style | Key Features | Notable Example |
|---|---|---|
| Deconstructivism | Irregular shapes, fragmented design | Dancing House, Prague |
| Future-focused | Inspired by science, innovative ideas | The Atomium, Belgium |
| Brutalism | Exposed concrete, bold expressions | Habitat 67, Montreal |
| Contemporary Green | Blends nature, eco-friendly design | Bosco Verticale, Milan |
Fun and Strange Buildings
Some architects let their imaginations run wild, creating buildings that are as surprising as they are playful. These unusual designs turn functional spaces into eye-catching works of art.
Longaberger Basket Building, Ohio, USA
In 1997, The Longaberger Company did more than think outside the box; they thought inside a basket. Their Newark, Ohio headquarters is a seven-story replica of the company's Medium Market Basket, blown up 160 times. Designed by NBBJ and Korda Nemeth Engineering, this 180,000-square-foot structure features heated handles to prevent icing during winter - a detail as practical as it is quirky. With a $30 million price tag, the building became a towering symbol of the company's pride in their handcrafted products.
"We wanted our corporate headquarters to reflect what our company is all about - making handcrafted baskets with pride", said Dave Longaberger, the company's founder, during the building's 1997 dedication ceremony.
The Crooked House, Poland
Fitting right into a storybook, the Krzywy Domek (Crooked House) in Sopot, Poland, is a visual delight with its warped, melting-like walls and windows. Inspired by the whimsical works of illustrators Jan Marcin Szancer and Per Dahlberg, this 2004 creation feels surreal yet welcoming. Inside, it's a bustling center of activity, housing restaurants, shops, and even a radio station, proving that quirky design can mix with practicality.
Stone House, Portugal
The Casa do Penedo in Portugal offers a blend of nature and ingenuity. Built in 1974, this house is nestled among four massive boulders that double as its walls and foundation. Concrete binds the stones together, forming a cozy retreat with a prehistoric vibe. Originally intended as a family hideaway, it has since transformed into a tourist magnet, drawing visitors eager to see its perfect harmony with nature.
WonderWorks, Orlando, Florida
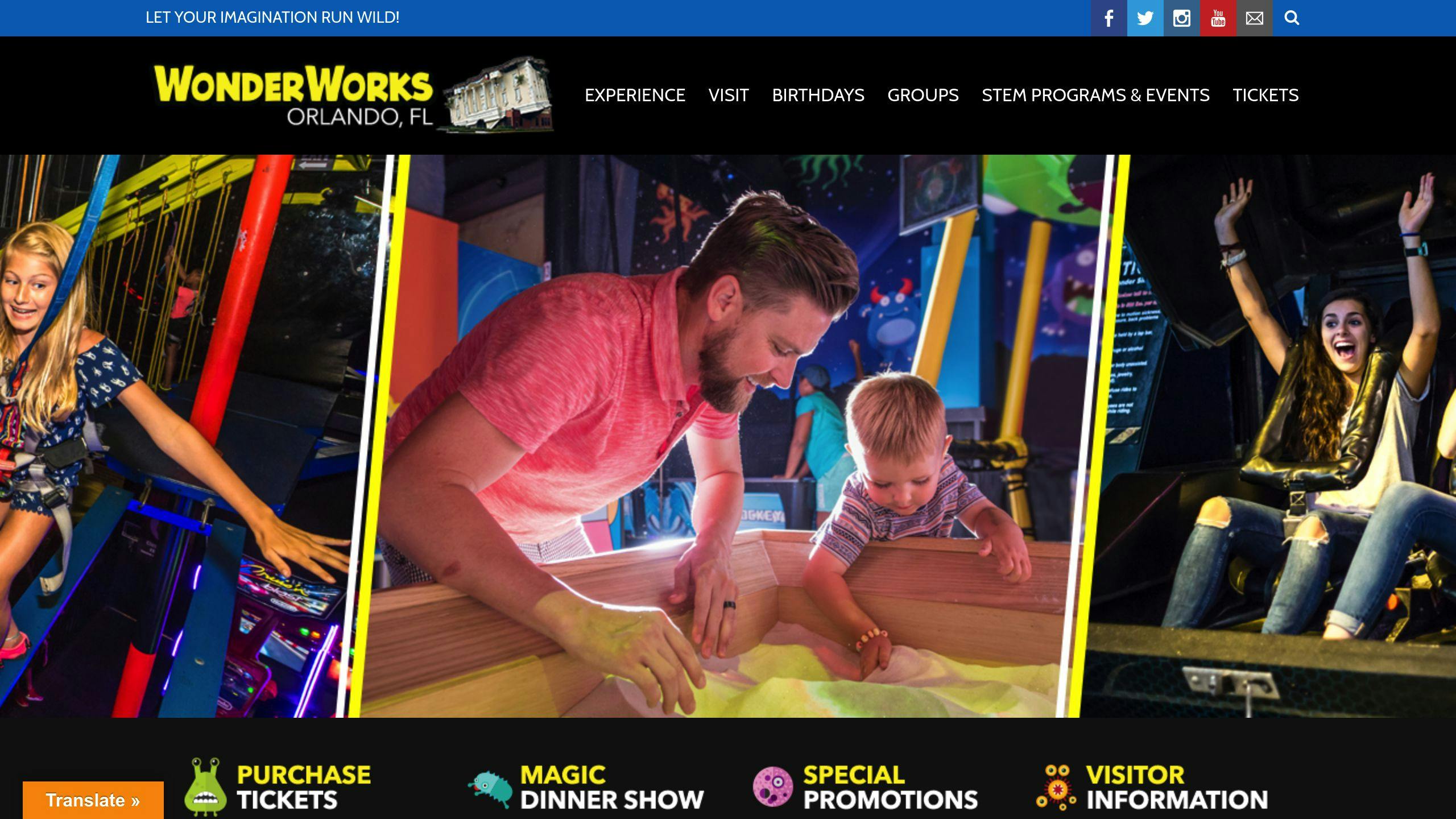
Orlando’s WonderWorks flips expectations - literally. The building looks like it’s been dropped roof-first into the ground, complete with upside-down palm trees and details that scream “topsy-turvy.” Opened in 1998, this structure suits its theme perfectly: a fictional lab where experiments have gone hilariously awry. Unsurprisingly, it’s become one of the most photographed spots in the city, living up to its dazzling first impression.
| Building | Location | Year Built | Unique Feature |
|---|---|---|---|
| Longaberger Basket | Newark, Ohio | 1997 | Giant replica of the company’s basket |
| Crooked House | Sopot, Poland | 2004 | Playfully warped, fairy tale-inspired design |
| Stone House | Fafe, Portugal | 1974 | Built into natural boulders |
| WonderWorks | Orlando, Florida | 1998 | Entire building constructed upside down |
sbb-itb-1be9014
New Tools for Building Design
Modern architecture is increasingly reliant on advanced technology, enabling architects to create designs that push the limits of imagination and engineering. These advancements are changing the way we conceptualize and construct extraordinary buildings.
Computer Design and AI
The use of advanced computer-aided design (CAD) software and artificial intelligence (AI) is reshaping the creative process for architects. AI can analyze vast data sets to fine-tune building designs, taking into account factors like energy use, structural stability, and environmental conditions. This helps architects bring to life intricate designs that would be nearly impossible to develop manually.
Digital twins, or virtual replicas, have added a new dimension to building design. These tools let architects simulate and evaluate a building’s performance in real-time, from energy usage to structural behavior. By testing their concepts digitally, architects can refine bold ideas long before construction begins, saving time and resources.
New Building Materials
Innovative materials are enabling designs that were once unthinkable. A striking example is the Eden Project in Cornwall, UK. This architectural marvel uses ETFE (Ethylene Tetrafluoroethylene) hexagonal panels to create its biodomes. These panels weigh just 1% of traditional glass, offer better insulation, and are highly durable.
| Material Type | Features | Example Use |
|---|---|---|
| ETFE Panels | Extremely lightweight, excellent insulation | Eden Project, UK |
| Smart Glass | Automatically changes transparency levels | Modern office spaces |
| Sustainable Composites | Eco-friendly and long-lasting | Environmentally-conscious constructions |
These materials not only expand the possibilities of design but also provide practical benefits, such as improved durability and energy efficiency.
3D Printing Buildings
3D printing is shaking up the construction industry by drastically cutting build times and costs. In 2014, the company WinSun showcased the potential of this technology by 3D printing 10 houses in a single day, setting a new benchmark for speed and innovation in construction.
"The construction 3D printing market is expected to skyrocket from $1.4 billion in 2020 to an estimated $14.1 billion by 2027, with an annual growth rate of 33.7%", according to industry analysis.
Beyond speed, 3D printing allows for the creation of complex, flowing designs that would be expensive or unattainable with conventional methods. Architectural visions involving intricate details and organic shapes can now come to life without the usual limitations of traditional construction techniques.
Final Thoughts
Architecture does more than enhance aesthetics - it shapes cities and embodies the essence of communities. Take the Guggenheim Museum in Bilbao, Spain, for example. This iconic building didn’t just become a breathtaking landmark; it also triggered an economic revival for the city, proving how striking design choices can redefine urban landscapes.
Today’s architectural efforts increasingly merge cultural traditions with sustainable practices. The Lotus Temple in New Delhi stands as a great example, blending Indian symbolism with modern engineering. Its unique design doesn’t just symbolize unity and progress; it also captivates millions of visitors from around the world every year.
"Architecture is not just one thing. It is not just an art. … It has to deal with the real situation; it has to do something good for the society." - Xiaodu Liu
This quote perfectly sums up how architecture goes beyond aesthetics to impact social and cultural life.
With the integration of advanced technologies, architecture is constantly evolving. Buildings now showcase both a respect for heritage and the adoption of environmentally-conscious features. For instance, using sustainable materials and energy-efficient designs demonstrates how modern architecture balances cultural significance with pressing environmental needs.
| Architectural Purpose | Example | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Economic Transformation | Guggenheim Museum, Bilbao | Boosted tourism and city revival |
| Cultural Representation | Sydney Opera House | Global symbol of identity |
| Environmental Awareness | Green building initiatives | Lower emissions and greater efficiency |
Looking ahead, architecture will continue to bridge the gap between traditional design and modern innovation. Sustainable materials, cutting-edge technology, and fresh approaches to construction will redefine what architecture can achieve - from honoring cultural roots to meeting future challenges head-on. These structures won’t just represent human ingenuity; they’ll point the way toward a more thoughtful, sustainable future.
Try Architecture Helper
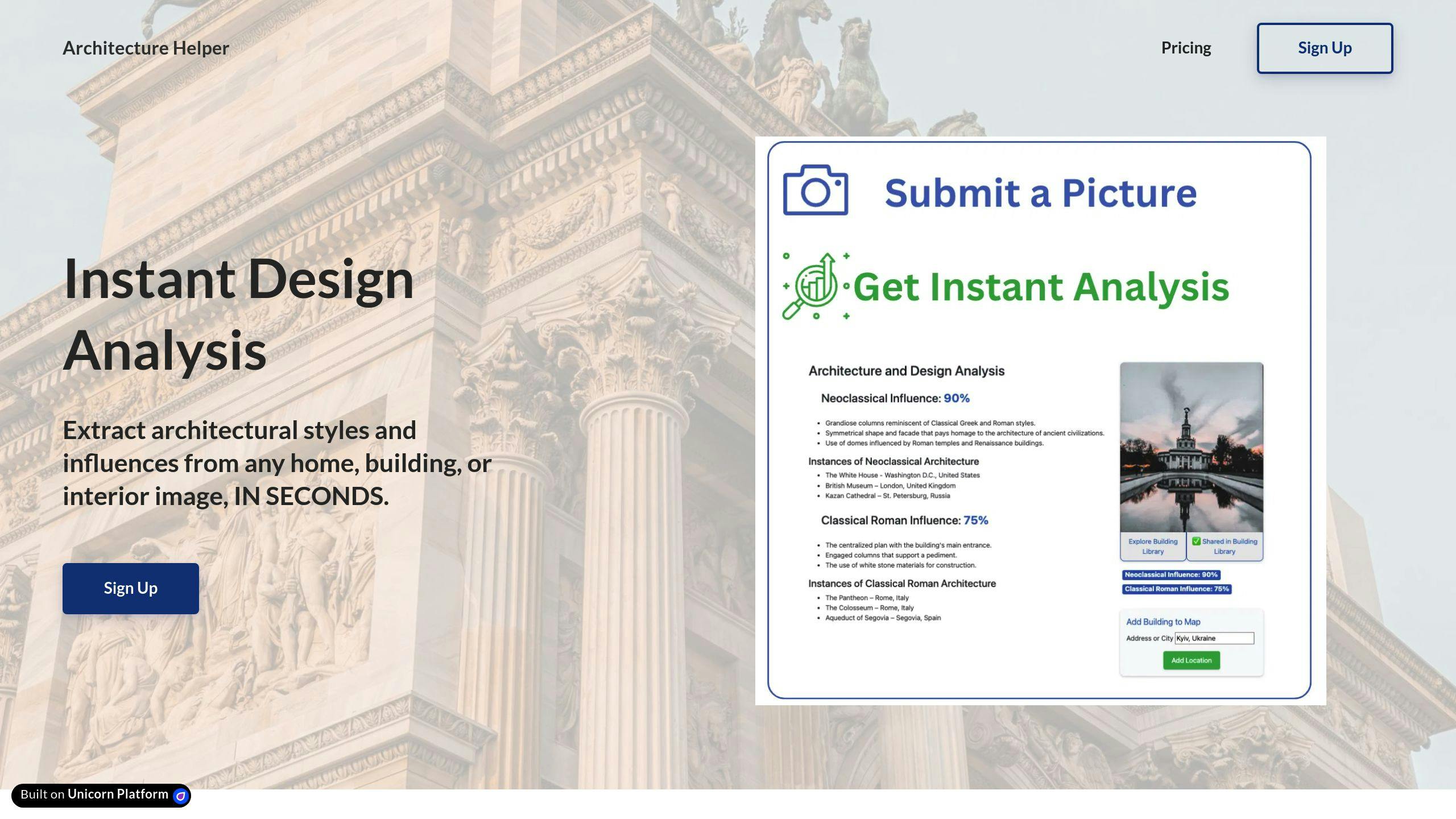
Architecture Helper provides a straightforward way to dive into architectural designs using its AI-driven photo analysis tools. Snap a picture of a building, and the platform helps identify its style, design influences, and standout features in no time.
With an extensive library packed with detailed analyses of real structures, it's a go-to resource for architecture buffs. You can discover key architectural elements and learn how these contribute to a building's overall look and feel. For example, when analyzing iconic landmarks like the Guggenheim Museum or the Sydney Opera House, Architecture Helper breaks down the elements that make these designs distinct, explaining the thought process behind them.
A standout feature is the design generation tool. This tool allows users to play around with architectural components, mixing and matching them to create completely new concepts. It’s an interactive, hands-on way to see how varying styles and details work together - and the possibilities are endless.
| Feature | Purpose | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Photo Analysis | Identifies architectural styles quickly | Offers a fast understanding of designs |
| Building Library | Provides real-world examples | Learn from legendary architectural works |
| Design Generator | Combines different design elements | Experiment with fresh ideas effortlessly |
The platform acts as a learning hub and a creative playground, ideal for anyone from hobbyists to seasoned professionals. Whether you're analyzing world-famous buildings or brainstorming ideas for your own projects, Architecture Helper has the tools to help deepen your design expertise.
If you’re curious about what’s trending in architecture today, Architecture Helper frequently updates its database with new buildings and insights on contemporary designs. By blending a rich historical archive with modern examples, the platform ensures you're always in the loop with cutting-edge architectural concepts. It’s a must-have for anyone intrigued by the art of building design.
FAQs
What is the most unique building in the world?
Though opinions may vary, a few buildings are celebrated for their extraordinary designs. The Guggenheim Museum in Bilbao, Spain, stands out with its bold titanium curves and unconventional architecture. The Sydney Opera House in Australia, with its sail-like shells, serves as a global icon of modern design. Meanwhile, Singapore's Marina Bay Sands, with its ship-like structure perched on three towers, is a striking example of how contemporary architecture can reshape urban landscapes.
What are the most impressive structures ever built?
Many structures around the world are awe-inspiring, thanks to their architectural brilliance and cultural value. The Taj Mahal in Agra, India, is renowned for its marble artistry and perfectly balanced design that continues to draw admiration. The Burj Khalifa in Dubai holds the record as the tallest building in the world, showcasing advanced engineering. London's Palace of Westminster represents the finest example of Gothic Revival design, while New York’s Solomon R. Guggenheim Museum challenges traditional building concepts with its spiral form.
What is the most futuristic building?
Modern architecture is consistently redefining what’s possible. Rio de Janeiro’s Museum of Tomorrow stands out with its soaring, cantilevered roof that seems to float. The Atomium in Brussels is another standout, resembling a massive molecular structure. East London’s The Crystal sets a new standard for eco-friendly design with its angular glass exterior, while Taipei’s Tao Zhu Yin Yuan incorporates a twisted architecture inspired by DNA strands.
"The Longaberger Basket Building in Ohio shows how architecture can break the mold. Completed in 1997, this seven-story structure features a glass-covered atrium, a central ceiling of natural light, and even heated handles to prevent ice - striking a balance between whimsy and functionality."
If you’re curious about unusual buildings, consider Architecture Helper’s photo analysis tool. This platform offers a database of global architectural styles and insights into design elements, helping users better understand what makes these iconic buildings stand out.


